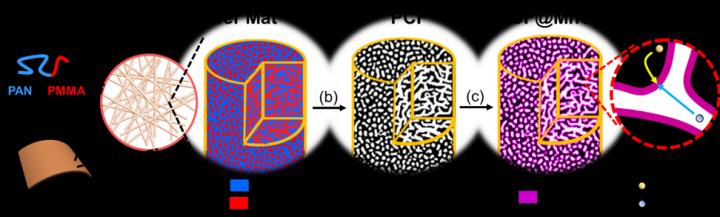
This figure shows the synthesis of porous carbon fibers and loading of MnO2. (a) A diblock copolymer of polyacrylonitrile-block-polymethyl methacrylate (PAN-b-PMMA) is spun into a polymer fiber mat. In the magnified view, the block copolymer microphase separates into a bicontinuous network structure. (b) After pyrolysis, the block copolymer fibers are converted to porous carbon fibers (black) with continuous and uniform mesopores (white channels), which afford high loadings of transition metal oxides. (c) The porous carbon fibers are loaded with manganese oxide (magenta). In the magnified view, the continuous carbon fiber matrix and partially filled mesopores provide effective expressways for electron conduction and ion diffusion, respectively.